TL;DR|Key Points on Earning with DeFi
- The essence of DeFi earning: earning market-driven returns by providing liquidity, lending assets, or contributing to network security.
- Main methods include staking, lending, and liquidity mining.
- Returns are driven by real demand, while risks mainly involve smart contract vulnerabilities, price volatility, and operational complexity.
- Compared to traditional finance (TradFi), DeFi earning requires no intermediaries, allows self-custody of funds, offers real-time interest accrual, and enables flexible strategy combinations.
- For beginners, using a DeFi yield aggregator (such as BenPay DeFi Earn) offers a friendlier, low-barrier entry into DeFi participation.
In the traditional financial world, our money often sits idle in low-yield savings accounts while banks profit handsomely from it. DeFi (Decentralized Finance) has fundamentally changed this paradigm, allowing anyone with an internet connection to become the “bank” itself. Through a variety of innovative mechanisms, crypto assets can generate ongoing yields. This guide provides a systematic explanation of DeFi earning mechanics, mainstream strategies, and safe practices using BenPay DeFi Earn as an example, helping you take control of your financial journey.
1. Where Does DeFi Crypto Earn Passive Income, and Is It Safe?
Simply put, every crypto you earn in DeFi is not some “digital illusion.” Like in the real world, returns follow the principle of “those who provide value, earn rewards.” Your yield comes from contributing essential services to decentralized networks, earning clear and transparent market-driven returns.
1.1 Providing Liquidity: Becoming an “Automated Market Maker” and Earning Trading Fees
When you deposit assets (e.g., USDC and ETH) into a liquidity pool, you essentially open an unattended trading window in a “public marketplace” accessible to everyone. Your funds facilitate instant trades for others, keeping the market liquid and efficient. In return, trading fees generated by the pool are automatically distributed proportionally to your contribution. The busier the pool, the higher your share. This transforms idle assets into productive capital, directly participating in market activity.
1.2 Lending Assets: Acting as a “Global Bank” and Earning Interest
You can deposit idle assets such as stablecoins into lending protocols like Compound or Aave. This is akin to placing your funds in a “global bank” operated by code, which lends to those in need. Your interest is determined by real-time supply and demand: more borrowers mean higher rates. Loans are typically over-collateralized and automatically liquidated to control risk, but during extreme market conditions, oracle failures, or network congestion, liquidation may be delayed, posing systemic or bad debt risk.
1.3 Contributing to Network Security: Staking Tokens and Earning Rewards
Blockchains like Ethereum and Solana use proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, relying on token holders to stake assets to secure network operations. When you stake tokens (e.g., ETH), you effectively back the network’s reliability and participate in consensus. Rewards come from block emissions (inflation) and transaction fee sharing. This is both an investment and a contribution to building network infrastructure. Misbehavior or node failures may lead to partial slashing of staked assets.
The Economic Logic Behind DeFi Earnings
Whether from trading fees, lending interest, or staking rewards, DeFi earnings stem from the demand for capital and network services. As long as on-chain transactions, lending, hedging, and asset allocation occur, yield opportunities exist.
However, it is also necessary to understand that when market activity declines and the demand for leverage weakens, the overall return level will also fall in tandem. Therefore, DeFi returns are not fixed-rate products but rather floating returns that change with the market environment.
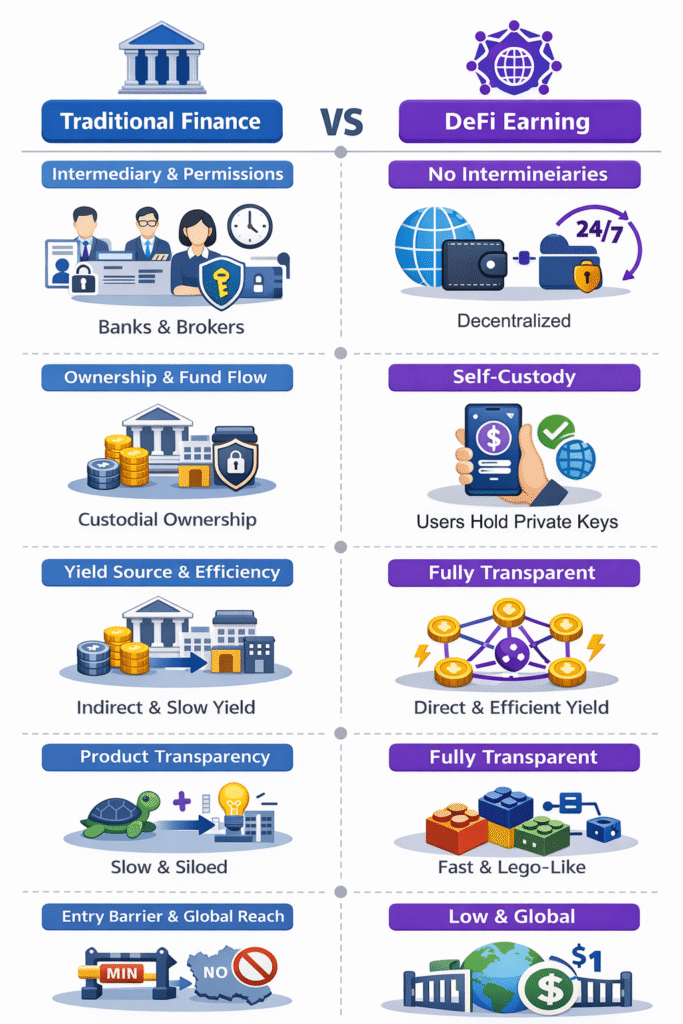
2. DeFi Earning vs. Traditional Finance: What’s the Difference?
In traditional finance, capital efficiency is often constrained by time and procedural limitations. DeFi reconstructs the logic of earning through blockchain technology, transforming idle capital into real-time productive assets. Understanding these differences is key to seizing next-generation financial opportunities.
- Traditional Finance (TradFi) is like depositing money in a large, closed reservoir. The flow of water (assets) is strictly controlled by the administrator (bank). You need to apply it to generate electricity from water (earn income), and efficiency depends on the administrator’s dispatching speed.
- DeFi Earning involves placing assets into a transparent and interconnected smart water network. The movement of every drop of water (asset) is clearly visible. You can automatically direct water to the places where it is most needed (such as borrowing and providing liquidity) through smart contracts, receive real-time returns, and freely combine various pipelines (protocols) to maximize the efficiency of water (capital) utilization.
Core Differences
| Dimension | Traditional Finance (TradFi) | Crypto DeFi Earn |
| Intermediary & Permissions | Centralized control: banks, brokers, fund managers. Account opening, verification, and business hours required. | Permissionless: anyone with a wallet can access it 24/7, globally, without identity verification. |
| Ownership & Fund Flow | Custodial: funds managed by institutions; you trust their security and compliance. | Self-custody: assets remain fully under the user’s private key; interact directly with smart contracts (“on-chain assets, on-chain yield”). |
| Yield Source & Efficiency | Indirect, layered: from interest margins, dividends, or capital gains. Transfers and settlement are slow, creating idle periods. | Direct, efficient: from protocol incentives (liquidity mining) and network usage fees. Assets can participate in multiple yield strategies in real-time (“instant compounding”). |
| Product Transparency | Opaque: portfolio composition, underlying assets, and risks are complex to verify. | Fully transparent: all smart contract codes, pool size, rates, and transaction history are publicly auditable on-chain. |
| Innovation & Composability | Slow, siloed: new product cycles long; limited cross-institution integration. | Fast, Lego-like: protocols (lending, trading, derivatives) can seamlessly combine to create automated yield strategies (“yield farming”). |
| Entry Barrier & Global Reach | High barrier, localized: minimum investment required; subject to local regulations and financial infrastructure. | Low barrier to entry, global: often possible to start with minimal assets (e.g., $1) and instantly access global markets. |
3. DeFi Crypto Earn Methods & Beginner-Friendly Options
3.1 Lending – Acting as a “Bank.”
- Mechanism: Deposit crypto assets (USDC, ETH) into protocols like Compound or Aave. Your funds enter a pool for borrowers, and you earn floating interest based on market demand. Stablecoins often provide more stable returns.
- Suitable for: Users seeking cash flow from idle assets and relatively steady strategies.
- Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities, liquidation anomalies, liquidity risks during extreme market events.
3.2 Staking – Basic “Deposit Yield.”
- Mechanism: Lock specific tokens (ETH 2.0, SOL) in a protocol to validate transactions and maintain network security. Rewards come from block issuance and transaction fee distribution.
- Suitable for: Long-term holders of major tokens who believe in ecosystem growth.
- Risks: Lock-up periods, inability to sell during market drops, and smart contract vulnerabilities.
3.3 Liquidity Mining – Becoming a “Market Maker” for Multiple Yields
- Mechanism: Deposit two tokens proportionally (ETH/USDC) into a DEX pool (Uniswap, Curve) to provide liquidity. Earn trading fees, protocol incentives, and arbitrage benefits.
- Suitable for: Advanced users willing to assume market risk for higher combined returns.
- Risks: Impermanent loss — temporary losses compared to holding assets if price ratios change sharply. Stablecoin pairs reduce impermanent loss but may still face risks from de-peg or protocol failures.
From Single Strategy to Strategy Combination: The Emergence of Yield Aggregators
When mechanisms such as lending, staking, and liquidity mining start to be combined, cross-chain scheduled, and automatically reinvested, a single protocol is no longer sufficient to cover the optimal path. Thus, the DeFi Yield Aggregator came into being. This type of tool enables users to indirectly participate in yield farming without directly engaging in complex operations.
4. Comparing DeFi Crypto Earn Methods
There are significant differences among various DeFi earning methods in terms of income sources, risk structures, and operational thresholds. Staking is more inclined towards the returns of the network layer. Lending and interest generation rely on the supply and demand of the capital market. Liquidity mining is part of yield cultivation, and its returns are tied to market activity. The yield aggregator integrates multiple yield sources through automated strategies, lowering the operational threshold for users to participate in complex strategies.
To have a more intuitive understanding of the income structure and risk levels of different methods, you can refer to the following table:
| Method | Yield Stability | Complexity | Main Risk | Beginner-Friendly |
| Staking | Medium | Low | Lock-up, price volatility | Low |
| Lending | High | Low | Contract risk | Medium |
| Liquidity Mining | Medium–High | High | Impermanent loss | No |
| DeFi Yield Aggregator (BenPay) | High | Very Low | Protocol combination risk | High |
5. Why Beginners Should Use Aggregators
With more protocols and complex strategies, single protocols are insufficient to capture optimal yields. Users would otherwise need to frequently shift funds across chains and protocols — essentially performing “yield farming.” Core challenges include:
- Multi-chain wallet management
- High Gas fees
- Protocol selection complexity
- Difficulty in risk diversification
DeFi yield aggregators address these challenges, allowing beginners to participate with reduced operational complexity and risk.
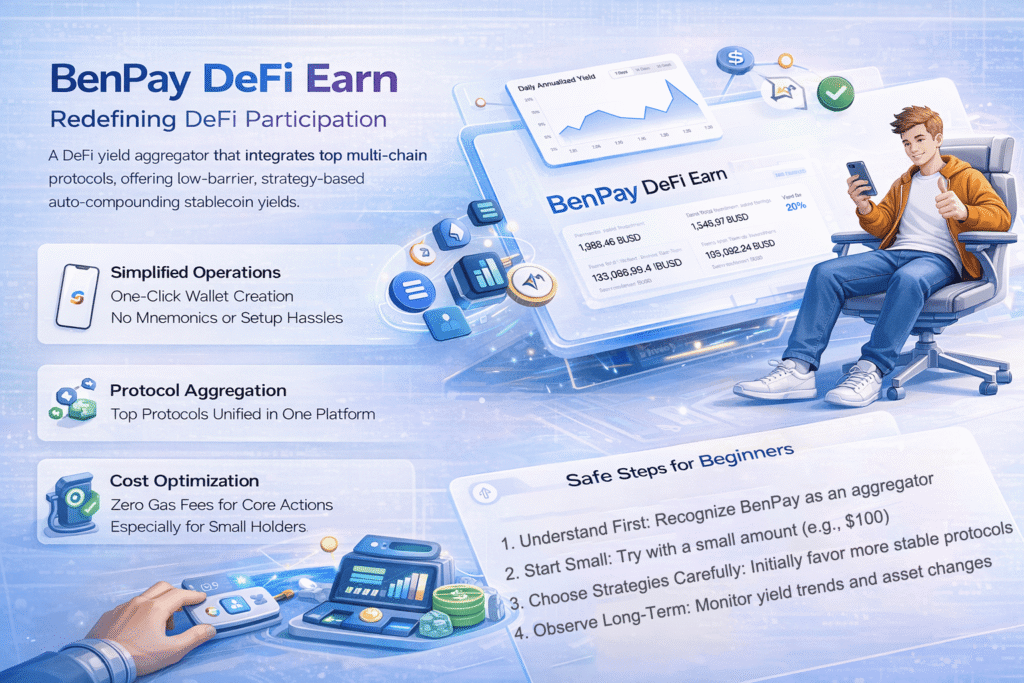
6. BenPay DeFi Earn: Redefining DeFi Participation
BenPay DeFi Earn is a DeFi yield aggregator that integrates top multi-chain protocols, offering low-barrier, strategy-based auto-compounding stablecoin yields. Its streamlined design consolidates multiple protocols into a single entry point, letting users enjoy on-chain yields safely and conveniently without deep technical knowledge.
6.1 Core Pain Points in DeFi Participation& BenPay Solutions
Traditional DeFi requires managing multiple wallets, understanding complex strategies, paying for gas fees, and monitoring market risks — demanding time, knowledge, and creating operational barriers. BenPay simplifies this through:
- Simplified Operations: One-click BenPay self-custodial wallet creation with Apple/Google accounts; no long mnemonic backups or complex wallet setups.
- Protocol Aggregation: Seamless access to Solana, AAVE, Compound, Morpho, Sky, Ethena, and other top protocols without switching interfaces.
- Cost Optimization: Core operations are exempt from gas fees, lowering costs, especially for small holders.
6.2 How to Participate in DeFi Earnings on BenPay
BenPay simplifies the complex on-chain asset allocation into four clear and simple steps, truly realizing the vision of “zero-basis participation in DeFi“.
- Connect Wallet: Create a BenPay wallet via Google/Apple account.
- Deposit Assets: Choose stablecoins and deposit across 10+ chains (Ethereum, Solana, Tron, BSC, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, etc.).
- Earn Yield: Select an amount and review protocol terms; yields settle daily, fully transparent.
- Partial Redemption: Withdraw fully or partially according to protocol rules.
All backend complexities — cross-chain transfers, gas fee payments, auto-compounding — are handled by audited smart contracts, giving users a simple interface and relatively stable returns without technical burden.
6.3 Safe Steps for Beginners
- Understand First: Recognize BenPay as an aggregator; yields come from underlying protocols and are market-dependent.
- Start Small: Try with a small amount (e.g., $100) to experience connection, deposit, and yield monitoring.
- Choose Strategies Carefully: Initially favor more stable protocols with moderate APY fluctuations.
- Observe Long-Term: Monitor yield trends and asset changes, and gradually adjust allocations.
Conclusion: From User to Network Contributor
DeFi earning transforms participants from passive “depositors” into active market builders and value sharers. It represents the democratization of finance, but requires knowledge and caution. BenPay DeFi Earn exemplifies a key evolution: moving from tech-driven experimentation to user-focused, secure, and stable products. By removing technical barriers, it makes on-chain asset allocation simple and accessible.
For beginners, success lies not in chasing the highest APY, but in understanding risks, verifying processes, starting small, and learning continuously. Taking that first step means you are not only earning yield but contributing to the evolution of on-chain financial infrastructure.
Risk Disclaimer
DeFi yields stem from on-chain financial activity and are not principal-protected products. Risks include smart contract bugs, protocol anomalies, stablecoin de-pegging, extreme market volatility, and network congestion. Yield aggregator products, while improving usability, also expose users to underlying protocol risks. Users should fully understand mechanisms, assess personal risk tolerance, and take responsibility for on-chain operations.

